Sales Tax Bulletin - No. 35
STB 35
Goods for use by registered Primary Producers-
This document has been Withdrawn.View the Withdrawal notice for this document.
Date of Issue: 1 September 1998
Valid from 1 September 1998
| Produced by the Withholding & Indirect Taxes Program of the Australian Taxation Office. |
About this bulletin
This bulletin explains how the sales tax laws apply to primary producers who have a sales tax registration number. It is a public ruling for the purposes of section 77 of the Sales Tax Assessment Act 1992 and may be relied upon by any person to whom it applies. It replaces any previous private or public rulings, if they are inconsistent with this bulletin, and is current as at 1 September 1998.
Warning: We regularly revise our publications to take into account changes in the law so if you are seeking to rely on anything contained in this bulletin, you should make sure that this edition is the latest.
If, after reading this bulletin you need more information on how the sales tax law affects your business, contact the Tax Office on 13 28 66 for the cost of a local call.
Personal computer goods and related equipment
Certain information contained in this bulletin may not apply to dealings with personal computer goods and related equipment (Part 7A goods). Legislation, which has received the Royal Assent, introduced new rules for dealing with these goods.
Broadly, these new rules include:
- • applying to the Tax Office for accreditation before you can buy Part 7A goods tax free for resale. This accreditation process will need to be supplemented by a requirement for a quotation of a sales tax registration number to be authorised by the Tax Office; and
- • the procedure for quoting a sales tax registration number or an exemption declaration when buying Part 7A goods for your own use.
A Helpline, telephone number 1 800 634 905, has been set up to answer questions about the new legislation and the administrative arrangements. Further information on Part 7A goods is also available at the Tax Office Internet website at www.ato.gov.au.
What you need to know about using your sales tax number
A sales tax registration number can be used by you to buy certain goods free of sales tax. You need to know:
- • which goods you can buy free of sales tax;
- • which goods you can't buy free of sales tax; and
- • how to use (i.e. quote) your sales tax registration number correctly.
What if I haven't started business yet?
If you have registered for sales tax because you intend to carry on a business of primary production, and you have purchased goods tax free, the first use of the goods must be after you have commenced business.
For example, you may buy a chain saw free of sales tax to use when you begin your primary production business. If you intend to use the chain saw in a hobby or private pursuit prior to the business commencing, the chainsaw will not qualify for exemption.
Which goods can I buy free of sales tax?
Not all goods used in relation to your business can be bought free of sales tax. There are three tests that must be met before you can buy goods tax free.
Step 1: Allowable activities
In order to buy goods free of sales tax they must be for use mainly in one or more allowable activities.
Allowable activities can be split into two groups:
- • primary production activities (see What are primary production activities? on page 3); and
- • ancillary or supporting activities (see What are ancillary or supporting activities? on pages 3 & 4).
Step 2: The 'MAINLY' test
To buy goods free of sales tax you must intend to use the goods mainly in respect of one or more allowable activities.
Mainly means to the extent of more than 50% of the goods overall use.
For example: If a wheat farmer uses equipment 75% of time in planting and harvesting wheat, the mainly test is satisfied.
You can count the use of goods in more than one allowable activity to make up more than 50% use.
For example: You may buy a stock trailer that you will use 35% of the time to feed out hay, 25% to transport stock around the property and 40% in transporting stock to market for sale (not an allowable activity). The trailer qualifies for exemption as it is mainly used in allowable activities.
Step 3: The 'STATUTORY PERIOD' test
To buy goods free of sales tax, you must intend to use the goods for the 'statutory period'.
The statutory period is 2 years or for the working life of the goods if that is less than 2 years.
In the case of most motor vehicles, the statutory period is the earlier of 2 years or 40,000 kilometres. For certain vehicles used mainly in transporting livestock exclusively in remote areas (as defined), they must be used for 2 years or their working life, whichever is less.
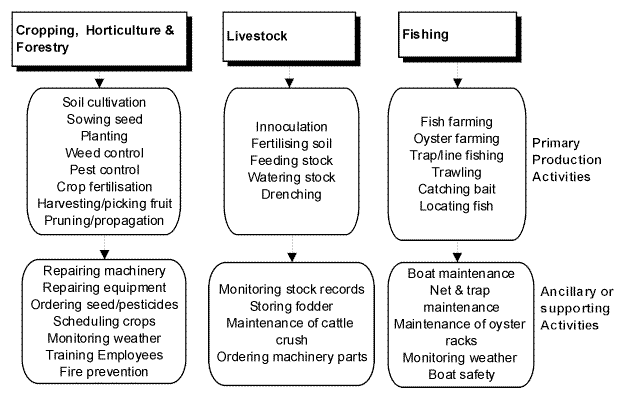
What are primary production activities?
These are activities which are directly linked to your primary production operation. They are the tasks you carry out that directly result in the creation of your primary products.
Some examples of primary production activities in relation to several types of farming are illustrated in diagram 1 below.
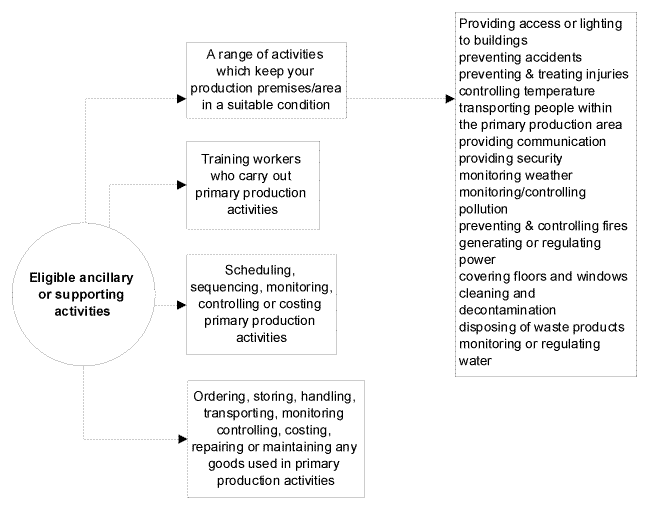
What are ancillary or supporting activities?
These are activities that support your primary production operations.
They include activities one step removed from the actual production process (see diagram 2 on page 4).
Which goods can't I buy free of sales tax?
Some goods cannot be bought free of sales tax by a primary producer even though they may be used in the primary production business, including:
- • most motor vehicles that are used off the property, e.g. on public roads, including trucks, family sedans and 2 wheel drive utilities. For special conditions that apply to certain four wheel drive vehicles, motor cycles, trailers and livestock carriers used mainly in agricultural industry see What about motor vehicles? on page 5.
- • goods used mainly in domestic or staff amenities, e.g. a stove for shearers' quarters or hand towels for the workers' wash room;
- • goods used mainly in activities of a personal or domestic nature relating to yourself or family members, e.g. a computer used mainly for children's studies and entertainment;
- • goods used mainly to carry out general administrative activities, e.g. a computer used mainly to record information used to prepare taxation returns; and
- • construction equipment, e.g. a circular saw used mainly to construct a hay shed.
What about motor vehicles?
There are two categories of motor vehicles that can be bought free of sales tax:
- • road vehicles used exclusively (only) on your property; and
- • certain vehicles for use mainly in agricultural industry.
Road vehicles used only on your property
Any road vehicle (except 2 wheel drive luxury cars) can be bought free of sales tax providing it is used mainly for primary production purposes, and:
- • always remains on your property; or
- • only goes off the property when going between adjacent properties that you own or control.
Important points
- • In general, use of these vehicles on public roads (other than travelling to adjacent or adjoining properties via the roadway) disqualifies them from exemption.
- • In the case of rural landholders, adjacent properties generally mean properties that are separated by very short distances, e.g. by a small piece of land of one other property holder, by a railway line or by a public road. Properties that are separated by suburbs, towns or properties of several other farmers are not adjacent.
- • However, occasional, irregular or insignificant use outside the property, e.g. for necessary servicing of the vehicle or in emergency situations, would not disqualify a vehicle from exemption from tax.
For example: You can't buy your farm truck (or truck parts) free of sales tax if it is used on public roads to transport produce to market. You can buy your farm truck (and truck parts) exempt of sales tax if it is only used on your property, for primary production purposes.
Certain other vehicles for use mainly in agricultural industry
- a. four wheel drive vehicles, e.g. tray bodies and utilities;
- b. agricultural motor cycles; and
- c. trailers and livestock carriers.
A description of the above goods appears below.
Agricultural industry does not include forestry (apart from plantation timber operations), fishing (including fish farming) or pearling (see What are primary production activities? on page 3).
These types of vehicles can be used on public roads, and still be purchased tax free, but they must:
- • be used mainly in carrying out activities in agricultural industry; and
- • satisfy steps 2 & 3 for sales tax exemption (see page 2).
a. Four wheel drive tray bodies and utilities
- • four wheel drive vehicles with a body type of jeep, platform, pick-up or utility. This includes most 4x4 utilities including dual cabs, but not 4x4 sedans or station wagons.
b. Agricultural motor cycles
- • motor cycles that have been designed for use on farms.
c. Trailers and livestock carriers
- • trailers (but not including motor vehicles or semi-trailers); and
- • livestock carriers designed for use with vehicles. This includes trailers towed by vehicles and stock crates for attachment to vehicles.
Parts, accessories and attachments for these vehicles can also be bought free of sales tax.
Key points to remember
- 1. You can only quote your sales tax registration number to buy goods that you are allowed to buy tax free (following the 3 steps for exemption). If you quote to buy goods tax free when you are not entitled to, sales tax will be payable, based on the price you paid for the goods. Further penalty taxes may also apply.
- 2. If you authorise another person to quote your sales tax registration number on your behalf, they must have enough knowledge of your business so that they can speak with authority about how the goods being acquired free of sales tax will be used.
- 3. You must only quote your number in the correct format.
|
I hereby quote Sales Tax Registration Number: Name of person authorised to quote: Signature of person authorised to quote: Date: |
- 4. You must know when your number is being used. If you have given your supplier a periodic quotation you could, during the period covered by this quotation, buy some goods that don't qualify for exemption. If you know this before buying the goods, you should tell your supplier that you are not claiming exemption. If you buy goods free of sales tax and then use them in such a way that they don't qualify for exemption you will have to pay sales tax to the Tax Office.
- 5. Ensure that the 3 tests ('allowable activities', 'mainly' and the 'statutory period' tests) are satisfied when buying goods free of sales tax.
- 6. If you cease being a primary producer, e.g. the business is sold, then you need to advise the Tax Office so we can cancel your registration number. You will also need to cancel your number and apply for a new one if you set up a different business structure, e.g. change the composition of a partnership or move from a partnership to a company.
- 7. Do not rely solely on retailers' advice regarding eligibility of goods for sales tax exemption. You are in the best position to know how the goods are to be used.
- 8. Do not rely solely on the advice of other primary producers in relation to the eligibility of goods for exemption. Their circumstances may be different to yours.
- 9. The fact that particular goods are treated as deductible for income tax purposes does not automatically mean that those goods will qualify for sales tax exemption, e.g. goods used in marketing and selling your produce.
- 10. Having a primary producer registration sticker on a particular motor vehicle does not automatically qualify the vehicle for sales tax exemption.
- 11. Suppliers cannot be compelled to sell for a tax free price. Where you have paid sales tax on goods that you were entitled to buy free of sales tax, you may apply to the Tax Office for a refund. It should be noted that only refunds totalling $200 or more requested within 3 years of using the goods will be considered by the Tax Office. Individual claims below this amount should be retained and added together until they total $200 or more. A sales tax refund form can be obtained by telephoning 13 28 66 or calling at the Tax Office.
Checklist
To further assist you in determining which goods qualify for exemption, we have developed a quick reference checklist for you to use. You can pin it up near your phone, or carry it with you in the glove box of your car. The checklist also shows you how to quote your sales tax number in order to claim exemption. The checklist is available through our information services listed below.
Need more information?
If you have any questions or need more information about how sales tax applies to you, please contact the Tax Office:
- • by phone on our national enquiry number 13 28 66. You can ring this number from anywhere in Australia for the cost of a local call; or
- • in person by visiting the enquiry counter at the Tax Office. Tax Office addresses are listed in the TaxPack, and in your White Pages telephone directory; or
- • by A Fax from Tax, our 24 hour fax information service. Simply call 13 28 60 (local call cost) on your phone or fax and follow the voice prompts; or
- • at our Internet website, at www.ato.gov.au
ATO references:
NO NAT 2739.9.98
